Systems of technical wood drying
Fresh air / exhaust air drying technology: proven technology, easy-to-use, high life expectancy
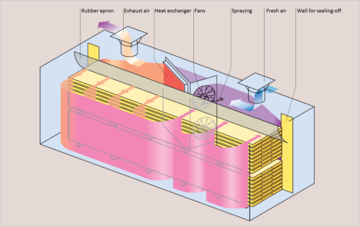
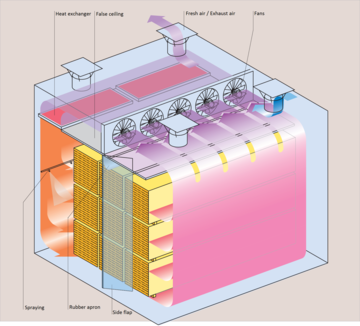
More than 90% of all timber dryers world-wide work according to the fresh-/exhaust air drying technology: Fans circulate warm air produced by a heating system (electric, hot water or steam) inside a steam-tight and thermally insulated room. The climate will be set and maintained accurately.
The air inside the chamber will be heated and the humidity will be raised by spraying of fine water or lowered by discharge of the moist air via the exhaust air flaps of the kiln.delivery of exhaust air outside through the air flaps. The result is an exact climate in the kiln for a controlled drying process to reach the desired final moisture content as well as the best wood quality. The kilns allow different ways of charging such as from the long side, from a face side or from the top.
Vacuum kiln drying
In vacuum kilns, a vacuum is generated inside the chamber and maintained exactly. This causes a reduction of the boiling point; the water is evaporated and thus the drying time shortened significantly. Only under the assumption that the drying process is a "continuous vacuum" (creating a constant underpressure even before heating) and the oxygen content is minimized, a discoloration-free drying of colour-susceptible woods is possible.
A vacuum kiln has a higher purchase price and more sophisticated technical equipment than a conventional drying chamber. Before making a purchase decision, it is necessary to check which amounts, types and dimensions of wood are to be dried in order to figure out if an economic advantage is given. The advantages of vacuum technology are greater, the thicker the wood and the higher the density of the wood, as well as the lower the desired final moisture shall be. In vacuum technology, charging takes place from the front.
Types of ventilation
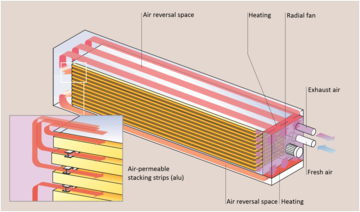
Longitudinal ventilation: timber drying along the wood fibre alignment
In dryers with longitudinal air flow, the air is sucked through the wood stack by a fan aligned on the front side. Each board is surrounded by the airflow from all four sides along its entire length. The air flows parallel to the wood fibers, according to the natural moisture flow in the wood. The high air speed possible with longitudinal ventilation guarantees uniform drying over the entire stack length. In order to allow the air circulation inside the wood stack, special, air-permeable stacking strips are required for the longitudinal flow drying.
Transversal (crosswise) ventilation: for large wood quantities
Wood dryers with several wood packages in height and width are ventilated transversal (cross wise) to the wood pile. Depending on the size of the chamber, several fans are installed and therefore chambers can be built in nearly every size.
In transversal ventilated drying chambers normal staple ledges of wood are used and pre-stacked pile packages can be directly loaded into the drying chamber.